Testing and Checking of GMDSS Batteries Required by SOLAS
GMDSS batteries are an important tool that provides power supply for GMDSS equipment operation in case of an emergency.
Regulation 13, Chapter IV of SOLAS sets the following requirements for GMDSS batteries:
- batteries must be recharged to the required minimum in less than 10 hours
- the batteries should provide power to operate GMDSS for 1 hour if GMDSS is getting the power from emergency generators
- for 6 hours if GMDSS is not getting the power from emergency generators
- the capacity of the batteries must be checked at less than 12 months
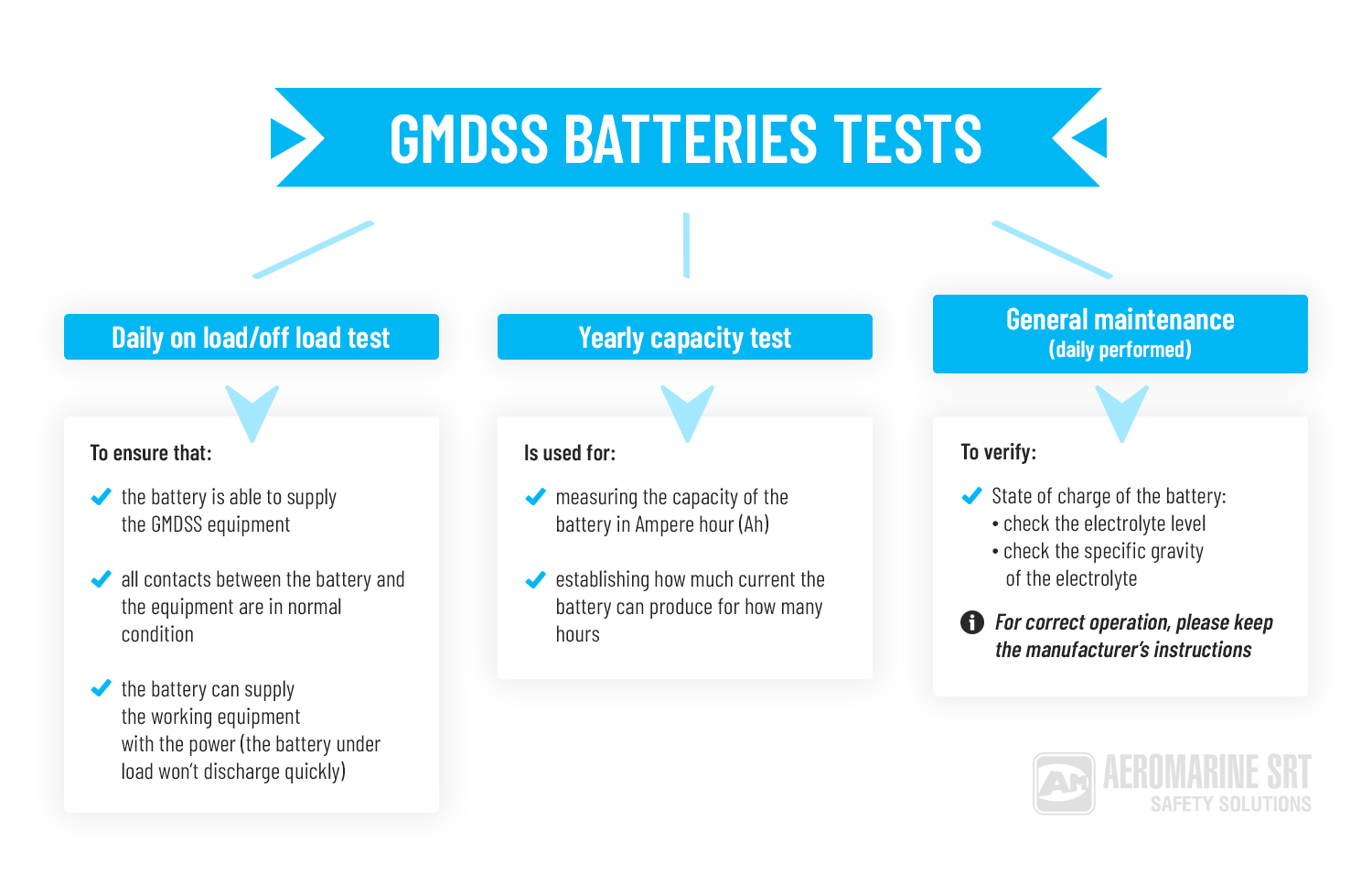
Surely, to be ready for an emergency, the batteries must be kept in proper condition. For this, they should be periodically tested and checked. There are three types of tests:
1. Daily on load/off load test, which ensures that all connections are intact and the voltage on loaded batteries do not drop too quickly.
2. Annual capacity test that measures the capacity of the battery in Ampere hours. The battery should be replaced if its capacity is less than 80% of the rated capacity.
3. General maintenance - measuring of the electrolyte level and the specific gravity.
Let's consider each of them in detail.
Daily On Load/Off Load Test
By this test we can ensure that:
√ all contacts between the battery and the equipment are in normal condition, and the GMDSS equipment can be powered by the battery;
√ the battery can supply the working equipment with the power, i.e. the battery won’t discharge quickly under load.
How to provide the battery on load/off load test
1. Disconnect the GMDSS station from the AC power supply by pressing the on/off button on the GMDSS panel (or in the radio room). Switch off all other power sources that charge the battery, if any. If the battery is being continuously charged, we will see no voltage drop. But by means of this test we intend to determine exactly the voltage drop.
NOTE: GMDSS equipment is mainly powered by AC batteries. The automatic disconnection of the AC power ensures that the batteries are not charged during the test. After the GMDSS equipment starts receiving battery power, the battery voltage should be recorded.
2. Press the PTT button to transmit on a non-distress and idle R/T frequency. Record the voltage under load when the PTT button is pressed.
3. Pay attention that the voltage drop shouldn’t exceed 1.5 volts.
Annual Capacity Test
This test is targeted to measure the capacity of the battery, as it tends to decrease with age.
To do this, we should charge the battery to full, then measure its capacity by discharging and applying the known load.
NOTE:
- The measure of battery capacity is not the voltage!
The capacity of the battery is measured in Ampere hour (Ah).
200 Ah means the battery can provide a current of 200 Ampere for one hour or 20 Amperes for 10 hours and so on.
Thus, the results of capacity test should answer the question: “How much current can a battery produce in how many hours?”
- A fully charged battery doesn’t mean that it can produce the rated capacity.
To illustrate the last point, let's see at a new smartphone and the one that has been in use for several years. A new cell with 100% charged battery works much longer than the used phone with a fully charged battery. This is due to the fact that the battery capacity decreases with age.
Preventing deep battery discharge
One of the SOLAS requirements concerns avoiding deep discharge of the battery while performing the capacity test.
Deep discharge means the least voltage a battery can have.
If the battery is discharged below this voltage level, there may be a situation when the battery may lose its capacity to a level where it cannot be used again.
For example, for nickel-based batteries, this voltage level is 1.0 V per cell. Thus, for 24 V battery pack (1.2 V x 20 cells), the deep discharge voltage level will be 20 V. So, when performing the capacity test, we should ensure that the battery voltage does not fall below 20 V or 1 V/cell.
Let's turn to the formula according to which
Power = Voltage x Current
The GMDSS battery is usually in the range of 200 Ah which is needed to give 24V.
To ensure that it still has 200Ah, we remove the batteries from charging and connections to GMDSS station (the existing load), then attach some known load to it. Usually a chain of several 100W bulbs is attached to the batteries terminals. So, if for example 6 bulbs (600W) are attached to the battery, it would receive 25A of current from the battery bank.
600 watts / 24 Volts = 25 Amp
When we apply the load to the battery bank, then we need to measure the voltage and the current across each battery bank terminal. We need to do it at least every hour.
The cases when we may stop the test:
1) The voltage drop in one battery cell is different than others. In thiscase the failing cell should be isolated. Then we may continue the test.
2) The battery has deep discharge voltage.
To avoid this, as per SOLAS, we need to measure the voltage of each cell during the test. The voltage mark of each cell should not be below 1V or 20V for the battery pack.
In this case we need to measure how much Ampere Hour has the battery delivered at this point.
NOTE: If it is less than 80% of its rated capacity, the capacity test has failed.
3) The test has performed for sufficient time to show that battery has 100% of its rated capacity. Say it has been 8 hours since the test started. And for 8 hours the current measure was 25A. So the battery has already delivered 200Ah (25A x 8 Hours). This shows that battery’s capacity is still 100%. In this case, this would conclude the test.
If this point is the reason of the stoppig of the test, then we make a conclusion that the battery is fine.
Charging the battery to 100% after capacity test
After we get sure that measured capacity is more than 80% of the rated one, we should measure the time required to charge the battery.
The percentage level of charged battery is determined by terminal voltage reading and the specific gravity of the electrolyte. For example, a 24V fully charged battery has a voltage of around 25.4V and specific gravity of 1.265. But we shouldn’t forget that the voltage can change depending on temperature, so specific gravity of electrolyte is more precise way to find out the state of battery charge.
After the capacity test, the measurement of the time a battery charges up to 100% should be done. Under SOLAS requirements this time should be less than 10 hours.
General maintenance of GMDSS batteries
The onboard batteries require no great maintenance. Just 2 parameters should be checked: the electrolyte level and the specific gravity of the electrolyte.

Checking the level of the electrolyte
It can reduce due to different reasons but it is important to maintain it according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
If the level is low, the battery cell should be filled with distilled water.
Checking the specific gravity of the electrolyte
Specific gravity of the electrolyte is considered more accurate measure of state of charge of the battery. It must be checked daily and recorded in battery log alonwith voltage. Specific gravity can reduce because of sulfation which causes the charging plates to be deposited with crystals. This causes reduction of holding charge and thus the capacity of the battery is reduced. BCI (Battery Council International) defines specific gravity of 1.265 as 100% state of charge. 1.225 is considered 75% state of charge. It is still better to refer to manufacturer’s instructions as some manufacturers can go upto specific gravity of 1.280 as the sign of 100% state of charge.
But if you have maintenance free batteries onboard, you do not need to check anything.




Be the first to comment