GMDSS Radio Survey Blog
The International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) is an international maritime agreement which requires Signatory flag states to ensure that ships flagged by them comply with minimum safety standards in construction, equipment and operation. The current version of the SOLAS Convention is the 1974 version, known as SOLAS 1974, which came into force on 25 May 1980. As at March 2016, SOLAS 1974 has 162 contracting States, which flag about 99% of merchant ships around the world in terms of gross tonnage.
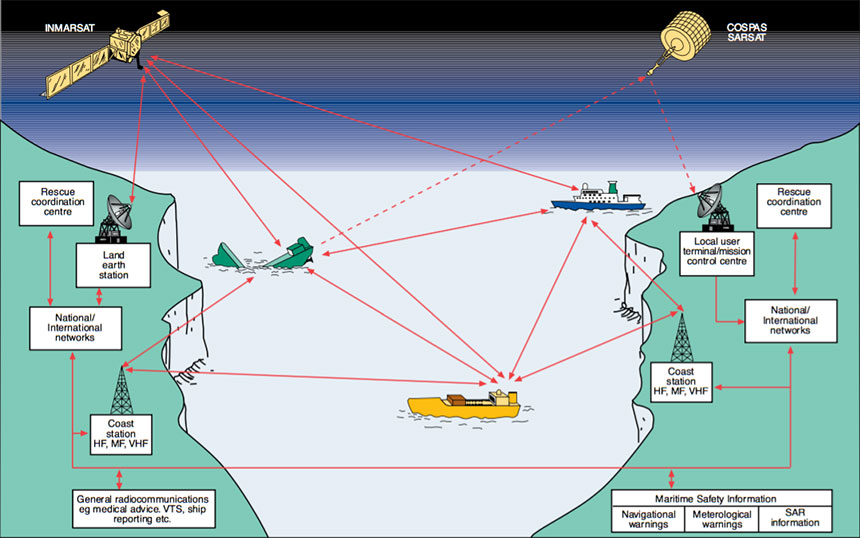
Amendments to the 1974 SOLAS Convention concerning radiocommunications for the GMDSS were published in 1989 and entered into force on 1 February 1992.