GMDSS Radio Survey Blog
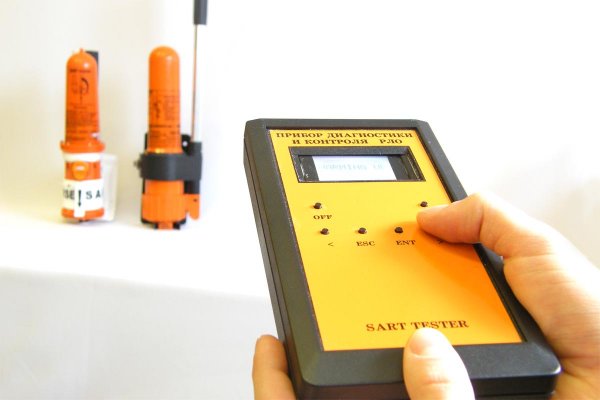
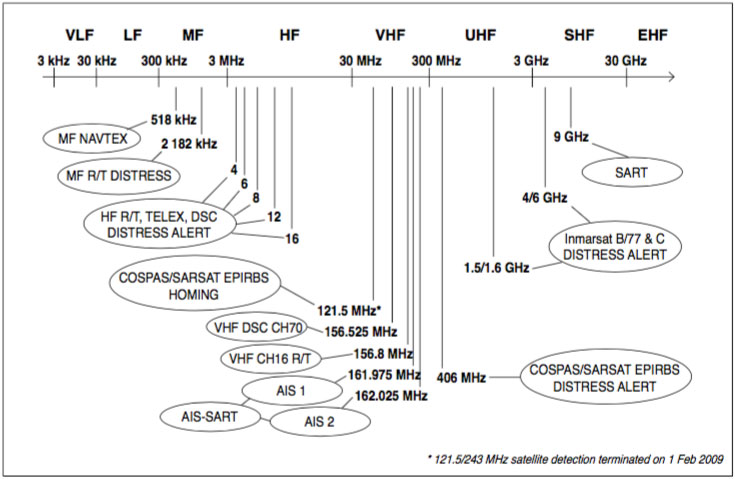
The Search and Rescue Radar Transponder as a part of GMDSS is a subject to annual test during radio survey. The annual testing of SART is recommended due to SOLAS regulation IV/15.8.
The purpose of an annual testing is to determine that SART is operational as defined in appropriate performance standards for Survival Craft Radar Transponders for use in Search and Rescue Operations, IMO Resolution A.802 (19).