GMDSS Radio Survey Blog
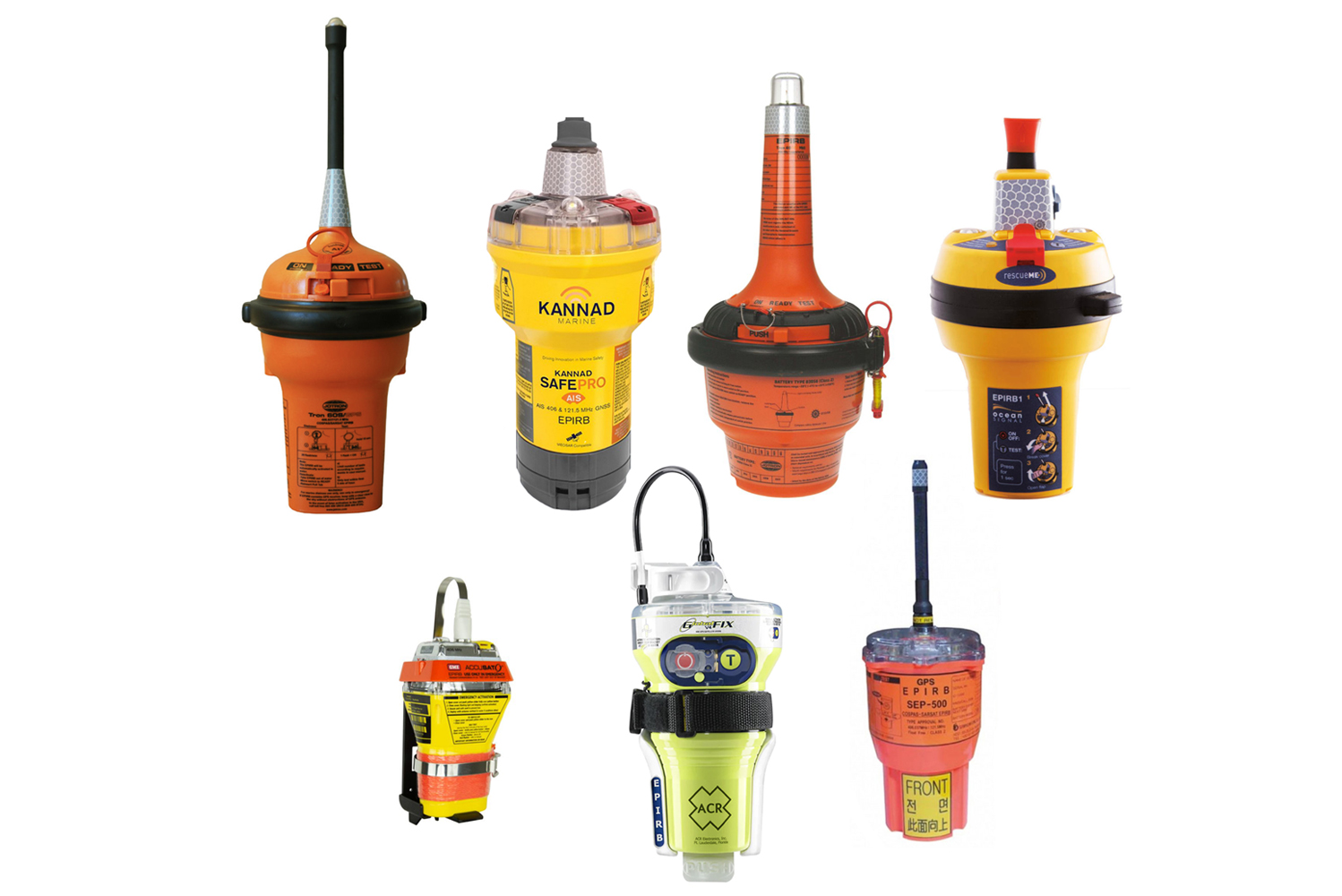
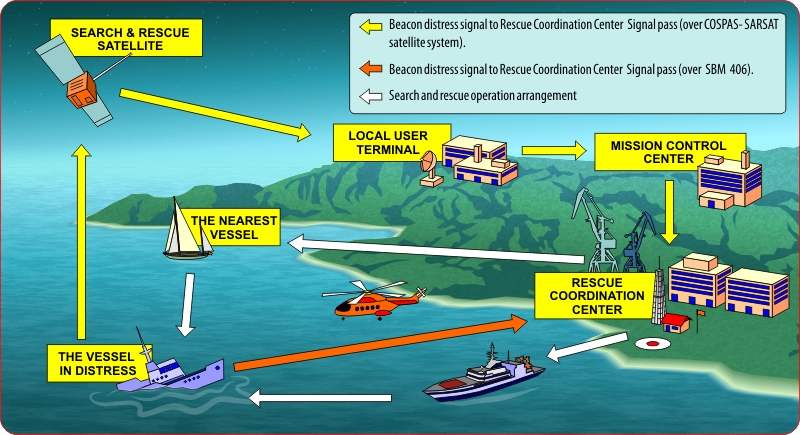
Since 1 January 2010, AIS – Search and Rescue Transmitters can be carried in lieu of Search and Rescue Radar Transponders on vessels subject to the 1974 SOLAS Convention.
The AIS-SART is designed to transmit AIS messages that indicate the position, static and safety information of a unit in distress. An AIS-SART has an integral position source (e.g. a GPS receiver) and accordingly, AIS stations receiving the AIS-SART signal are able to display the range and bearing to the AIS-SART.